Large Loop Excision of the Transformation Zone (LLETZ)
What is an LLETZ Procedure?
Large loop excision of the transformation zone (LLETZ) treats abnormal cell growth on the cervix, also known as cervical dysplasia. The procedure involves using a loop-shaped wire to remove a section of the cervical tissue that contains abnormal cells.
LLETZ is typically performed as a day surgery procedure under anaesthetic. Side effects may include pain, bleeding, and infection. It may also may have some impact on patients' future pregnancies and childbirth.
Common Names for LLETZ
LLETZ is also known by several other names, including:
- Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP)
- Cervical loop excision
- Cervical diathermy loop excision
- Diathermy loop cone biopsy
- Large loop excision (LLE)
LLETZ and LEEP are the most commonly used names for this procedure.
Who Should Undergo LLETZ?
LLETZ surgery is typically recommended for women with abnormal cervical cells, also known as cervical dysplasia. Cervical dysplasia is most commonly caused by a viral infection called human papillomavirus (HPV), which can lead to precancerous changes in the cervical cells.
LLETZ surgery may be recommended for women who have:
- Abnormal cervical cell changes found during a Pap smear test or cervical screening test (CST),
- A cervical biopsy that shows cervical dysplasia,
- Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN),
- Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS)
Additionally, LLETZ may be recommended for women who have previously had an LLETZ and have recurrent abnormal cervical cells.
Benefits of LLETZ Surgery
The main benefit of LLETZ is that it can remove abnormal cervical tissue and effectively treat cervical dysplasia, preventing the development of cervical cancer.
Some other benefits of LLETZ include the following:
- It is a relatively quick procedure that can be performed as a day surgery procedure, usually taking around 30 minutes to complete.
- Recovery time is usually short; patients can resume normal activities within a few days.
- LLETZ is considered a highly effective treatment for cervical dysplasia, with a high success rate of removing abnormal cervical tissue.
- It is minimally invasive, resulting in less bleeding, pain, and scarring than other treatments, such as a cold knife conisation.
- LLETZ preserves the patient's fertility, removing only the abnormal cervical tissue and leaving the healthy cervical tissue and uterus intact.
Alternative Options to LLETZ
There are several alternative options to LLETZ for treating cervical dysplasia, which include:
- Cryotherapy: This procedure involves freezing abnormal cervical tissue using a freezing probe. It is relatively quick and straightforward, but it may have a lower success rate than LLETZ.
- Laser ablation: This procedure involves using a laser to remove abnormal cervical tissue. It is considered less invasive than LLETZ and may have a slightly lower risk of complications but a somewhat lower success rate than LLETZ.
- Conization: This procedure involves using a scalpel to remove a cone-shaped piece of cervical tissue. It is considered more invasive than LLETZ and may have a slightly higher risk of complications, but it may have a higher success rate than LLETZ.
- Observation: This option is usually recommended for low-grade cervical dysplasia, which means abnormal cervical cells without signs of cervical cancer. Regular cervical screening and follow-up visits are needed, as some abnormal cells may persist or progress to precancerous or cancerous cells over time.
Preparation for LLETZ Surgery
Before the procedure:
- A patient will consult with a gynaecologist to discuss the procedure, the risks and benefits, and the recovery process.
- The LLETZ procedure is most commonly recommended based on abnormal cervical screening, colposcopy findings and cervical biopsy results. A patient will be instructed to avoid sexual intercourse, to douche, or to use any vaginal creams or medications for some time before the surgery.
- Patients will be instructed to prepare for the surgery, such as fasting for a certain period before the procedure.
What Happens During an LLETZ Procedure?
Here's what typically happens during an LLETZ procedure:
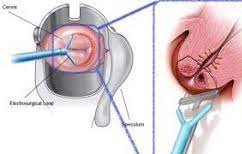
- You will be asked to lie on an examination table with your feet in stirrups to allow access to the cervix. The doctor will clean the area and may administer a local anaesthetic to numb the cervix.
- The doctor will insert a speculum into the vagina to hold the vaginal walls apart, allowing visualisation of the cervix.
- Using the LLETZ procedure, the doctor will pass a thin wire loop through the speculum and apply an electrical current to the loop. The current cuts and removes a thin layer of tissue from the cervix. The loop also acts to cauterise the blood vessels to minimise bleeding.
- The removed tissue will be sent to a laboratory for further examination. This helps in determining the presence and severity of any abnormal cells.
What to Expect After an LLETZ Procedure?
After the surgery:
- You will be monitored for some time after the procedure to ensure no complications, such as bleeding or infection.
- You may experience discomfort after the procedure, such as cramping or light bleeding.
- You may be given pain medication to help manage pain or discomfort.
- You will be instructed to avoid sexual intercourse, to douche, or to use any vaginal creams or medications after the surgery.
- You will be scheduled for follow-up appointments to monitor for any recurrence of cervical dysplasia.
LLETZ Aftercare
- You will have a vaginal discharge for up to three weeks
- Avoid intercourse and the use of tampons for three weeks
- Avoid swimming pools, spas, and baths – use the shower for three weeks
- Avoid heavy exercise, running and jumping for four weeks.
- Most women can resume normal daily activities within 1-2 days.
LLETZ Prognosis
The prognosis for LLETZ surgery is generally favourable, with a high success rate of removing abnormal cervical tissue and preventing the development of cervical cancer. Most patients will have complete removal of the abnormal cervical tissue after LLETZ surgery. However, LLETZ may only be suitable for some patients, and a patient's circumstances will determine the suitability of this procedure. In some cases, the abnormal cervical tissue may recur after LLETZ surgery, and additional treatment may be necessary.
LLETZ may also impact patients' future pregnancies and childbirths, and you should discuss these potential risks and benefits with Dr Crawford before the procedure.
Regular follow-up appointments and cervical screenings are essential after LLETZ surgery to monitor for cervical dysplasia recurrence and ensure the best outcomes.
LLETZ Risks
LLETZ is relatively safe, but certain risks are associated, like any surgery. Some of the risks related to LLETZ surgery include the following:
- Bleeding: Some bleeding is expected after the procedure, but heavy or prolonged bleeding may require additional treatment.
- Infection: LLETZ surgery carries a small risk of infection, which can commonly be treated with antibiotics.
- Pain: Some patients may experience cramping or discomfort after the procedure, but this is usually mild and can be managed with pain medication.
- Scarring: LLETZ surgery may cause some scarring of the cervix, but this is usually minimal.
- Preterm labour and delivery: LLETZ may increase the risk of preterm labour and delivery in future pregnancies.
Recurrence of cervical dysplasia: In some cases, the abnormal cervical tissue may recur after LLETZ surgery, and additional treatment may be necessary.
What if LLETZ is Delayed?
It is generally recommended that LLETZ surgery be performed as soon as possible after cervical dysplasia is diagnosed to prevent cervical dysplasia's progression to cervical cancer.
If LLETZ surgery is delayed, there is a risk that the abnormal cervical tissue may continue to grow and progress to cervical cancer. The longer the delay, the greater the chance the abnormal cervical tissue will progress to cervical cancer.
If LLETZ surgery is delayed, schedule regular follow-up appointments and cervical screenings to monitor the abnormal cervical tissue and detect any progression of cervical dysplasia. If the abnormal cervical tissue does progress to cervical cancer, the treatment options may be more invasive and significantly impact the patient's future fertility.
LLETZ Costs
The LLETZ procedure can be performed in a public hospital and private day surgery. If you are planning for care in the private sector, you will receive a surgical quote estimate before the procedure. If you have private health insurance, check your coverage with your fund to confirm any anticipated out-of-pocket costs.



